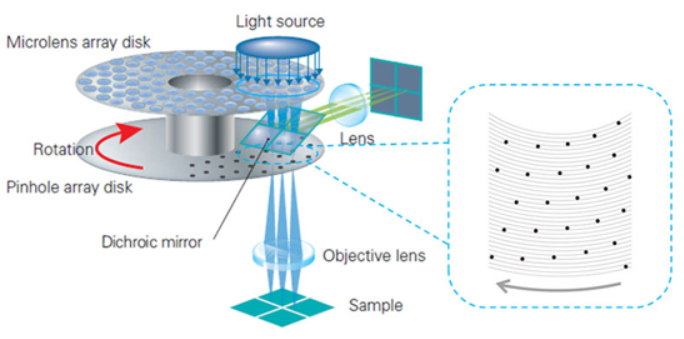
Spinning Disk Confocal Microscope Principle:
Laser scanning confocal microscopes focus a single beam on the specimen plane to sequentially point-scan a region of interest with spatial filtration of the emission light through a single pinhole that rejects light originating from regions that are out of focus (refer to Confocal Microscope Principle). Unfortunately, the single-beam laser confocal microscope is limited in image acquisition speed. For generalized imaging scenarios, confocal microscopes scanning rate is about one-half to two seconds per image, depending upon the dimensions. Thus, most laser scanning confocal microscopes are inadequate for capturing the millisecond dynamic events in living cells.
In Spinning disk confocal microscope, an expanded laser beam pass through the microlense and pinhole array disk to illuminate on the sample by multiple beam. When the disks spin, the multiple light points scan a field of view. The emission signal then pass through the pinhole array disk which remove out of focus signal, finally captured by a high sensitivity camera(sCMOS or EMCCD). The multiple beam scanning and the fast spinning speed can reduce the image capturing time and improve the time resolution, so spinning disk confocal microscope is helpful for imaging fast dynamic events in living cells.